Sep 5, 2020 | News
A biocide is intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a definition for biocides as “a diverse group of poisonous substances including preservatives, insecticides, disinfectants, and pesticides used for the control of organisms that are harmful to human or animal health or that cause damage to natural or manufactured products” (source https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biocide).
We rely on biocides for many things. For example, we disinfect our hands at hospitals to avoid spreading bacteria, and we use mosquito repellents to avoid nasty bites.
Almost all of the biocidal active substances have a relative high toxicity, Although the definition of biocides is quite strict, today during the Covid period little distinction is made at the layman level for disinfectants that contain high does of alcohols and approved biocides. One must follow all chemical handling and use recommendations.
EPA Registered Hard Surface Disinfectants Comparison Chart
The concerns with biocides
Attention to workers’ and visitors’ exposure to chemicals in the product selections, particularly respiratory and dermal irritants or asthmagens, is an important consideration. “Cleaning and disinfecting are important parts of a comprehensive infection prevention strategy. While demand for more effective cleaning and disinfecting is growing, there is also increasing evidence that exposure to cleaning and disinfecting can result in acute and chronic health effects, particularly respiratory illness.“ (Quinn et al, 2015). The authors do suggest more research is needed on how to weigh the type of cleaner used with the potential for occupational exposure with the type of cleaning and disinfection that is appropriate for a given area (Bello et al, 2009; Quinn et al, 2015). Some ideas to reduce occupational exposure are modifications to cleaning schedules, appropriate product selection, and ventilation to reduce exposure. Use of personal protective equipment is also important (Weber et al, 2016). During those years steam sanitizers were not available. Now they are.
Weber, D. J., Consoli, S. A., & Rutala, W. A. (2016). Occupational health risks associated with the use of germicides in health care. American journal of infection control, 44(5), e85-e89.
Bello, A., Quinn, M. M., Perry, M. J., & Milton, D. K. (2009). Characterization of occupational exposures to cleaning products used for common cleaning tasks-a pilot study of hospital cleaners. Environmental Health, 8(1), 11.
Quinn, M. M., Henneberger, P. K., Braun, B., Delclos, G. L., Fagan, K., Huang, V., … & Maher, K. A. (2015). Cleaning and disinfecting environmental surfaces in health care: toward an integrated framework for infection and occupational illness prevention. American journal of infection control, 43(5), 424-434.
Quinn, P. J., Markey, B. K., Leonard, F. C., Fitzpatrick E. S., Fanning, S., Hartigan P. 2011. Veterinary Microbiology and Microbial Disease. Second Edition. John Wiley & Sons.

Sep 4, 2020 | News
Source: https://www.aopa.org/news-and-media/all-news/2020/august/20/improper-disinfectant-appears-to-damage-two-skyhawks
Bayzi Corporation supports GA (general Aviation) aircraft users. If you think that the steam sanitation could work for you please contact us at Bayzi Corporation. We will be happy to arrange for a free one time Top-Off Sanitation for up to three GA small aircraft, per airport within 50 miles of our manufacturing plant (Cincinnati, OH), for all those who request it during September 2020.
This service is recommended by the GA pilot employees of Bayzi Corporation (Cincinnati USA).
Prior to making the request please familiarize yourselves with the information on Bayzi.com. The contact request is made here.*
Bayzi Corporation will provide a price reduction coupon to GA aircraft owners outside and in the Cincinnati area for the purchase of SaniZap® Units.
* The free top-off will be made only to non electrical, non avionics, non critical parts like the seats and carpets. Can be performed only under
the supervision of the aircraft owner.

Sep 1, 2020 | News
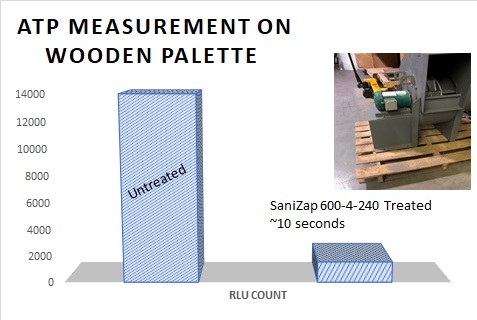
Can we quantify cleanliness? What is ATP?
This is commonly measured by an ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) test-meter that measures RLU’s (Relative Light Units) from swabbed regions. The number and types of bacteria present on a surface is of concern for infection control, but bacterial tests are sometimes very specific and do not yield the overall hygienic condition or cleanliness of a surface. RLU measurements on the other hand are more appropriate to define general cleanliness. ATP is a molecule found in and around living cells, and as such it gives a direct measure of biological concentration and health. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a molecule made up of an adenine ring, a ribose sugar, and most importantly 3 phosphates. In the most basic terms, this molecule is the body’s currency for all of its functions. Anything that the body does requires energy which all comes from ATP.The fats, carbs, and proteins that we eat are broken down and metabolized in order to replenish the used ATP in our bodies. One of the phosphates breaks off and releases a burst of energy. When this happens the molecule turns into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) because there is only 2 phosphates attached. Through a series of reactions another phosphate is attached and the molecule becomes ATP again. The ATP in our bodies are recycled after they produce energy.
ATP is quantified by measuring the light produced through its reaction with the naturally occurring enzyme luciferase using a luminometer. The amount of light produced is directly proportional to the amount of ATP present in a sample.
RLU (Relative Light Units) is the unit for measuring the ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). ATP has been found to be a sensitive indicator molecule for the presence of biological residues due to its universal presence in all living cells (microbes, animal and plant cells). When a test swab is activated, a bio-luminescent reaction occurs, generating light output. RLU measurements will vary for the type of meter. However, because the ATP bio-luminescence reaction is linear, the more ATP present, the higher the contamination- indicates poor hygiene and vice versa. The presence of ATP on the surface indicates that it has not been adequately cleaned. An increase in “dirt” (mostly biological residues) on a surface is displayed in an increase in the amount of ATP present on that surface. Thus ATP an effective marker for the assessment of the hygienic status of an environmental surface. RLU’s measure this ATP.
ATP tests (the RLU measurements) are not intended to replace microbial tests but there is often a direct correlation between the results of the two types of measurements when done concurrently.
It is a common mistake for users to expect a close agreement between RLU measurements when comparing different systems (different makes of RLU measurement meters). This is due to the differences in RLU sensitivity, scales and outputs and the inherent variation of this biological assay and variations from sample distribution and sample collection. Therefore the ATP hygiene test (RLU counts) should not be considered as a precision assay for bacterial counts. The ATP hygiene test application is a sensitive, direct, objective test of cleaning efficiency and risk. It is a quick risk analyzer that help you suspect if there is a need to do further laboratory tests for a more detailed test for bacteria and particular species of bacteria. Care should be taken when comparing the system performance from different instruments or suppliers. Comparisons ahould be made with the same test machines and conditions.
The RLU measurements are great to infer if the cleanliness quality of a test surface or object has changed or if a particular cleaning system has efficacy in improving cleanliness. It is not a quantitative test for bacterial counts as it indicates different information than a CFU count test does.
When using RLU it is common to define a threshold of cleanliness. This is subjective in the sense that it depends on the machine employed. In fact some studies show that there is poor correlation between active bacteria and ATP measurements. ( Colbert et. al. Healthcare Infection, 2015,20, 108–114 Researchhttp://dx.doi.org/10.1071/HI15011), However this test is used often.
Here is a chart from A suggested sampling algorithm for use with ATP testing for cleanliness measurement (by G.S. Whiteley, T.O. Glasbey, P.P. Fahey,
Volume 21, ISSUE 4,
P169-175, December 01, 2016 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idh.2016.11.003).Suggested cleanliness thresholds and corresponding RLU for 3 ATP device brands.

Last Page Vol. 3A
Aug 23, 2020 | News
This issue comes up often when comparing cleaning techniques. For example when comparing chemical use and duration to rapid clean steam.
Bleach often contains Sodium Hypochlorite — Sodium hypochlorite can cause severe eye irritation and if ingested can cause severe stomach irritation and sores. Sodium Hydroxide is also often used to stabilize household bleach. It is extremely caustic and can cause significant skin irritation if touched.
Other simple cleaners contains trace doses of 2-butoxyethanol — sustained inhalation of high concentrations (100-500 ppm) of this compound has been found to cause adrenal tumors in tested animals. Please consult toxicologists for a definitive analysis.
An non-intuitive feature of using chemicals over steam is noted in the energy usage. See for example (click).
Bacteria are becoming resistant to even powerful drugs like antibiotics. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_antibiotic-resistant_bacteria
How do bacteria become extremophiles in space.
A Ball of Bacteria Survived for 3 Years … in Space!
New research from the Japanese Tanpopo mission adds to scientists’ understanding of how living organisms can endure the hostile environment.
Read: https://apple.news/AxZnbdZKdRZOZJlF94O0qdA

- For COVID-19 and many other viruses one needs the surface to be in contact with a biocidal chemical for over 10 mins https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/reopen-guidance.html# See also https://extension.colostate.edu/docs/pubs/foodnut/kitchen-sanitize.pdf See also https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/health-and-wellness/2020/april/cleaning-against-covid See also https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/health-and-wellness/2020/april/cleaning-against-covid
- Warning bells are sounding for the overuse of chemicals. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5685540/ See also WHO says please do not spray disinfectants https://www.cnn.com/world/live-news/coronavirus-pandemic-05-16-20-intl/h_0f2325d2b58893ae656ac8e522afad79
- Protecting the environment from a new problem from harsh and greasy chemicals, is beginning to cause serious worries. https://www.cnn.com/world/live-news/coronavirus-pandemic-05-16-20-intl/h_0f2325d2b58893ae656ac8e522afad79

Aug 21, 2020 | News
Why is it important to clean the environment?
Microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses) are present throughout our environment and can cause infection. The environment can serve as a breeding ground for these organisms. Cleaning and disinfecting housekeeping surfaces and medical equipment, especially those that are frequently touched, is important to decrease and/ or prevent the spread of these organisms to people particularly if they are rapid acting pathogens. Human fungal infections may fail to respond to contemporary antifungal therapies in vivo despite in vitro fungal isolate drug susceptibility. Such a discrepancy between in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility and in vivo treatment outcomes is partially explained by microbes adopting a drug-resistant biofilm mode of growth during infection. High efficacy methods of high temperature steam may be one of the few solutions for surfaces infested with biofilms.
What should I worry about when doing such cleaning? Cleaning is important. Having a regiment is important. Preventing the spread of toxic chemicals is important. If you are a restaurant, rental car agency or any other commercial business it is also important to know the speed of removal and the frequency of the regiment. High temperature steam is one of the fastest methods.
Resource for Cleaning:
For COVID-19 and many other viruses you need to leave on surface for 10 mins https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/reopen-guidance.html# See also https://extension.colostate.edu/docs/pubs/foodnut/kitchen-sanitize.pdf See also https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/health-and-wellness/2020/april/cleaning-against-covid See also https://www.pennmedicine.org/updates/blogs/health-and-wellness/2020/april/cleaning-against-covid
Warnings are sounding for the overuse of chemicals. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5685540/
Protecting the environment from a new problem from harsh and greasy chemicals, is beginning to cause serious worries. https://www.cnn.com/world/live-news/coronavirus-pandemic-05-16-20-intl/h_0f2325d2b58893ae656ac8e522afad79
https://www.vdh.virginia.gov/content/uploads/sites/3/2016/03/Environmental-Cleaning-Fact-Sheet.pdf

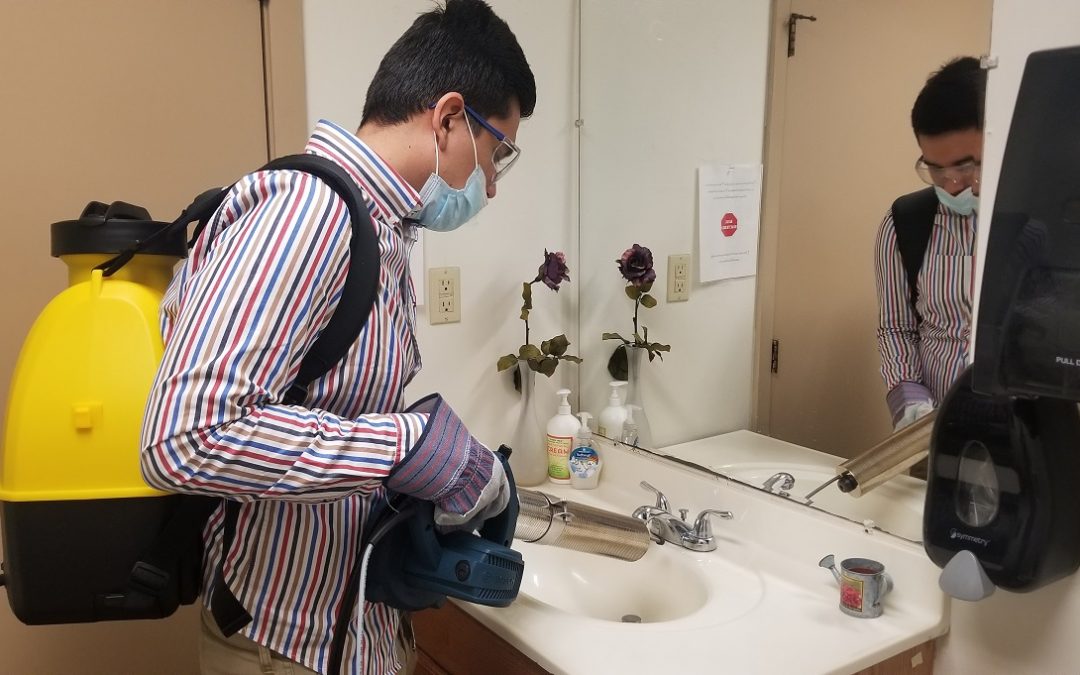
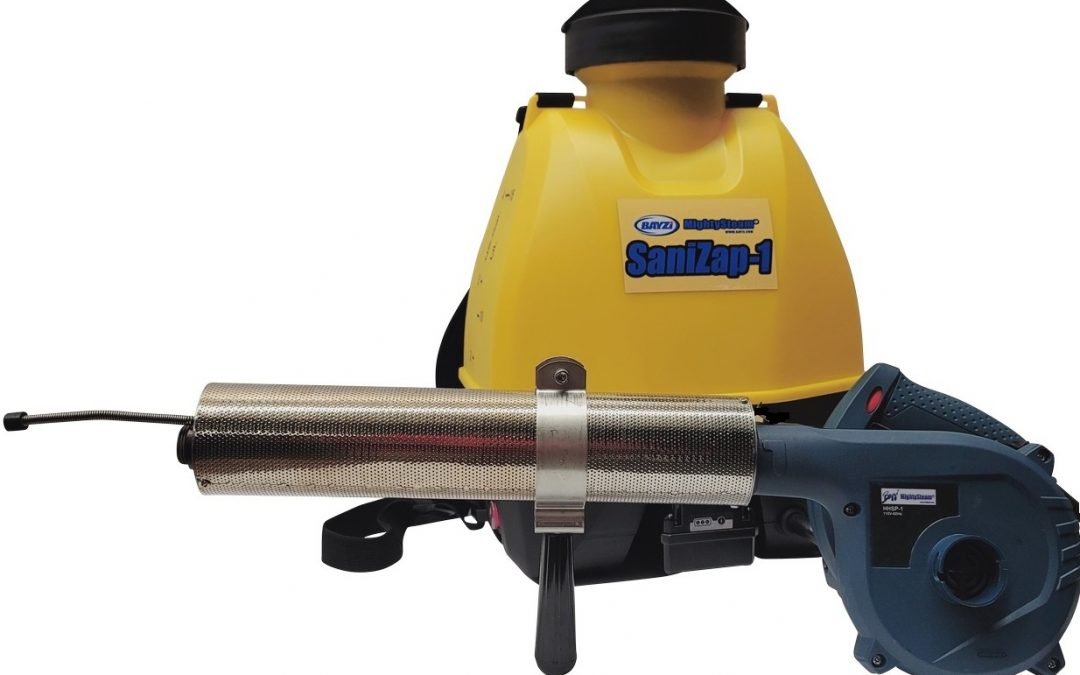
SaniZap-1

Aug 12, 2020 | News
The levels of clean
In a restaurant, there are at least three levels of cleaning: cleaning, sanitizing, and disinfecting and deep-cleaning. At the lowest level, cleaning means clearing dirt, trash, and debris from surfaces with a cloth. This makes the room and serving area look tidy and inviting, but it may not be enough to protect your guests. When done correctly, sanitizing kills 99% of bacteria, fungi, and some microbes. Sanitizing solutions must be mixed at the proper concentration and must be left on a surface for at least 60 seconds preferably more (but be aware of toxic chemicals). If you wipe down a table, menu, or serving counter with sanitizer and immediately dry it, you won’t get the full effect- you have to leave it there for minutes depending on the solution and dilution. Make sure your sanitizer does not cause corrosion. The highest level is sterility or close to ii is a good target. Some types of steam from rapid steam generators at high temperatures can get you there. But be careful not to burn anything. It is highly recommended that you work with a microbiologist if you wish these levels of cleaning. Be aware that sanitizers can cause damage. People use cloth or towels made of organic materials such as cotton or paper pulp. These materials break down sanitizer and will, over time, cause the solution to be ineffective. Rental Cars should be properly steamed with MightySteam for adequate residence.
High temperature steam like those obtained from SaniZap® act within a second to few seconds.
Use the cleanest possible methods for good hygiene. Routine cleaning and disinfecting are an important part of reducing the risk of exposure to COVID-19. Normal routine cleaning with soap and water alone can reduce risk of exposure and is a necessary step before you disinfect dirty surfaces.
Surfaces frequently touched by multiple people, such as door handles, desks, phones, light switches, and faucets, should be cleaned and disinfected at least daily. More frequent cleaning and disinfection may be required based on level of use. Source https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/reopen-guidance.html#. For more information on Restaurants https://www.nrn.com/operations/how-should-restaurants-clean-coronavirus-cases.
One problem of using some type of sugar based chemicals are that it attracts not only microbes but also small creatures (bed bugs and ants). High temperature steam like the MightySteam® works on both microbes and bugs.


Hard To Reach Biofilms